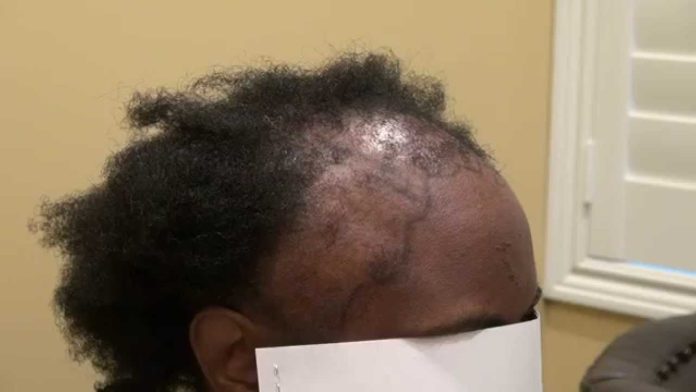
Hair loss happens for so many reasons, experts say. For instance, stress can culminate in hair loss, just as you can experience hair loss when you don’t eat nutritional diet.
Pregnancy also affects the hair, gynaecologists say. Many women have reported commendable hair growth during pregnancy, only for them to shed all the hair within weeks after delivery. This is even as many women have noticed stalled hair growth or outright hair loss, only for their hair to start growing normally after they have had their baby.
Physicians also caution, however, that certain medications can lead to hair loss, hence the need to always read drug labels for contraindications or, if in doubt, ask your doctor or pharmacist before you start taking a medication.
As hard as it may sound, hair loss sometimes includes eyelashes, eyebrows, and body hair. Ouch!
A hair’s life cycle
What many of us need to also know is that our hair has a life cycle. According to experts at the online platform, AARP, each hair on your head has its own individual life cycle.
“A strand grows between two and eight years. Then, in a period of two or three weeks, it stops growing and rests for three to four months before detaching from the follicle. Your head of hair is a mixture of 85 to 90 percent actively growing hair and hair that’s resting and waiting to shed,” AARP says.
Drug-induced hair loss
According to pharmacists, hair loss is a relatively rare side effect of certain medication, noting that certain medications such as beta-blockers, blood thinners, antidepressants, cholesterol-lowering drugs, certain non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and hormone-related drugs like thyroid medications, hormone replacement therapies or steroids can all make users to lose hair.
So, which medications cause hair loss?
Here are some of the types of medications that can cause hair loss as a side effect.
Vitamin A: According to experts at Heathline, high doses of vitamin A and medications derived from it can cause hair loss.
Acne medications: One type acne of vitamin A-derived medication, isotretinoin (Accutane) and tretinoin (Retin-A) can cause hair loss.
Antibiotics: Prescription antibiotics can cause temporary hair thinning. Antibiotics can deplete your vitamin B and hemoglobin, and thus disrupt hair growth.
When hemoglobin is too low, you can become anaemic and lose hair as a result. Normal levels of vitamin B are also critical to maintaining healthy hair.
Antifungals: Antifungal medications are indicated for fungal infections and have been linked to hair loss in some people. The antifungal medication voriconazole is one such treatment that has been associated with alopecia in the past.
Anti-clotting drugs: Anticoagulants like heparin and warfarin are used to thin the blood and prevent blood clots and certain health concerns in some people (like those with heart conditions).
Again, some medications can cause hair loss that begins after taking them for about three months. Such drugs include cholesterol-lowering drugs, immunosuppressants, anticonvulsants, blood pressure medications, antidepressants and mood stabilizers, weight loss drugs, medications for gout, chemotherapy, etc.
What you can do
Experts advise that if you’ve recently begun taking a new medication and have noticed hair thinning or loss, talk to your doctor about switching to another medication. They may be able to choose a medicine that doesn’t cause the same side effect. Your doctor may also recommend that you stop taking the medication for a few months.
The bottom line
In most cases, hair growth returns to its previous state once you’ve stopped taking a medication that causes hair loss. Adjusting the dosage may also ease symptoms of hair loss.
However, don’t stop taking a medication without discussing it with your doctor. There may be other options with fewer adverse side effects.