In a world where busy schedules and on-the-go lifestyles dominate, fast foods often present as the easiest solution to hunger.
Whether it’s the drive-thru, food delivery apps, or quick takeaway spots on every corner, fast food’s allure is primarily its convenience. But beyond the temporary satisfaction and the saved time lies a deeper issue: the effects of these meals on health. Understanding these effects becomes even more critical, especially for those who aim to adopt healthier lifestyles.
The attraction of a quick meal might be strong, but the long-term consequences on one’s body can be substantial. This article dives deep into what regularly indulging in fast foods does to your body and why.
 Weight gain: Fast food is notorious for its high calorie content. These meals often contain excessive amounts of fats, sugars, and salt. Regular consumption can lead to an imbalance in your daily caloric intake, contributing to unhealthy weight gain.
Weight gain: Fast food is notorious for its high calorie content. These meals often contain excessive amounts of fats, sugars, and salt. Regular consumption can lead to an imbalance in your daily caloric intake, contributing to unhealthy weight gain.
According to Mayo Clinic, consuming more calories than you burn inevitably results in weight gain.
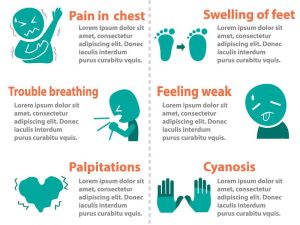
Increased risk of heart diseases: Fast food typically contains high levels of saturated and trans fats, which can raise blood cholesterol levels. Elevated cholesterol increases the risk of heart disease. The CDC states that high cholesterol can lead to fatty buildups in the arteries, heightening the risk of a heart attack.
Effects on liver function: Similar to the effects of excessive alcohol intake, an unhealthy diet that includes regular fast-food consumption can harm the liver. WebMD, a trusted online health platform, highlights that foods high in fats and sugar can cause fatty liver disease.
Poor digestion: The high fat content in fast food can be detrimental to digestive health. As Healthline points out, high fat intake can increase the risk of acid reflux and heartburn. Moreover, fast food lacks fiber, essential for regular bowel movements.
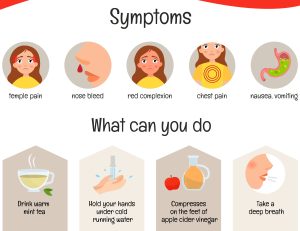
Increased blood pressure: Fast foods are often laden with salt, a primary contributor to high blood pressure. The Cleveland Clinic mentions that excessive salt intake makes it difficult for the kidneys to remove water, resulting in increased blood pressure.
Impact on respiratory system: Consistent consumption of fast food can lead to weight gain, which in turn can result in respiratory problems, including asthma. Online health publication Medical News Today confirms that obesity is a risk factor for asthma and other respiratory conditions.
Impact on skin health: You might not immediately connect fast food with skin health, but there’s a link. According to CVS, foods high in carbohydrates can exacerbate skin conditions, leading to acne and other skin problems.
Elevated blood sugar levels: Fast foods often contain high amounts of sugar and refined carbs, leading to rapid spikes in blood sugar. Over time, this can increase the risk of type 2 diabetes. The NIH highlights that a diet high in calories from any source contributes to weight gain, a significant risk factor for diabetes.
Impact on mental health: The foods we eat can affect our mental well-being. Online platform Healthline emphasizes the connection between diet and depression. Consuming high amounts of fast food, lacking essential nutrients, may contribute to a higher risk of depression.
Risk of dental problems: The sugars present in fast food can lead to dental problems. Walgreens states that frequent consumption of sugary foods and drinks is a primary contributor to cavities.
Conclusion
While the occasional fast-food treat might not be detrimental, it’s essential to be aware of the cumulative effects of regular consumption. By understanding the potential risks, women can make informed decisions about their diets, prioritizing health and well-being.


