The likelihood of falling ill or dying from diseases that resist treatment has escalated in Africa, with children and other vulnerable groups being most at risk, according to a new report by the Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention.
“The continent faces the highest mortality rate from antimicrobial resistance (AMR), with 27.3 deaths per 100,000 — exceeding the combined death toll from HIV-AIDS, tuberculosis, and malaria,” the African Union Landmark Report launched on Thursday at the Africa CDC headquarters showed.
Scientists warn that if AMR is not controlled effectively by 2050, at least one person will be dying every three seconds by then.
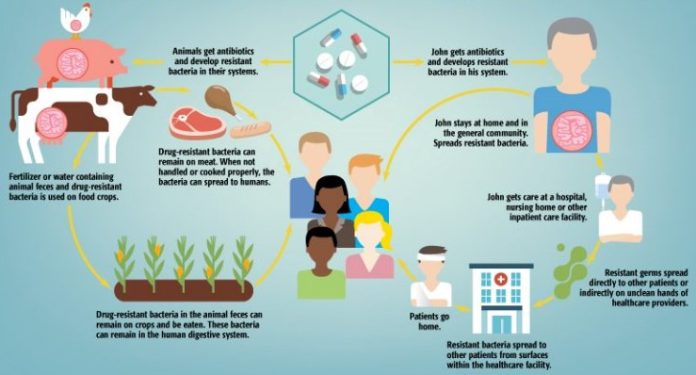
When germs do not respond to the drugs designed to kill them, infections that used to be treatable can become fatal
According to experts at the French multinational biotechnology company, bioMérieux Connection, antimicrobial resistance (AMR) happens when a germ develops or acquires a way to prevent the antimicrobial drug from effectively killing or controlling growth. When germs do not respond to the drugs designed to kill them, infections that used to be treatable can become fatal.
 “The name, ‘antimicrobial resistance,’ covers all types of germs, more scientifically called microbes, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses, that can cause infections. ‘Antibiotic resistance’ specifically refers to bacteria and does not include other types of germs. Bacteria cause most resistant infections, so the term, ‘antibiotic resistance’ tends to be more common,” the experts say.
“The name, ‘antimicrobial resistance,’ covers all types of germs, more scientifically called microbes, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses, that can cause infections. ‘Antibiotic resistance’ specifically refers to bacteria and does not include other types of germs. Bacteria cause most resistant infections, so the term, ‘antibiotic resistance’ tends to be more common,” the experts say.
They explain further that antimicrobial resistance, and more specifically, antibiotic resistance, has become a major threat to our society. Resistance continues to grow because of improper antimicrobial dosage and use.
AMR occurs when microorganisms like bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites develop resistance to antimicrobial drugs, a process hastened by human behaviors such as the misuse and overuse of these drugs in healthcare, agriculture, and food systems
“Antibiotics are among the most commonly prescribed drugs used in human medicine and can be lifesaving drugs. But doctors prescribe antibiotics sub-optimally up to half the time, either when not needed or with incorrect dosing or duration,” scientists say.

Consequently, the AU Landmark Report revealed that Africa bears a significant burden of infectious diseases, accounting for approximately 95 per cent of malaria deaths, 70 per cent of people living with HIV, and 25 per cent of TB deaths globally.
“We must not ignore this silent threat that disproportionately impacts the most vulnerable among us,” said Africa CDC Deputy Director-General, Dr. Raji Tajudeen.
AMR occurs when microorganisms like bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites develop resistance to antimicrobial drugs, a process hastened by human behaviors such as the misuse and overuse of these drugs in healthcare, agriculture, and food systems.
This renders antibiotics and other antimicrobials less effective, causing treatment failures, increased disease spread, severe illness, disability, and higher mortality rates.

“Despite the estimated $2-$6bn needed annually for an effective AMR response across Africa, current funding is only a tenth of that allocated to other major diseases. This underfunding makes AMR a significant barrier to sustainable development, hindering progress toward the Sustainable Development Goals, and the African Union’s Agenda 2063.
“An estimated 700,000 people die annually from drug-resistant infections globally. Without timely intervention, this number is projected to reach 10 million by 2050, with Africa accounting for 4.5 million,” a statement by the Africa CDC noted.
“Fighting disease requires resources and working with member states, and our partners we need to do all we can to save lives,” said Dr. Tajudeen, speaking at the launch of a report on AMR in Africa.
The event also initiated discussions on a roadmap and targets to advance Africa’s battle against AMR. The outcomes are expected to inform the upcoming United Nations General Assembly High-Level Meeting in September—a crucial platform for global action on this escalating crisis.
An estimated 700K people die annually from drug-resistant infections globally. Without timely intervention, this number is projected to reach 10m by 2050, with Africa accounting for 4.5m
Director of the African Union-Inter African Bureau for Animal Resources, Dr. Huyam Salih, emphasised the critical role that the AU must play in combating AMR. “Antimicrobial resistance is not just a health issue—it is a threat to our agrifood systems, food safety, food security, livelihoods, and economies,” she said.
By 2050, global healthcare costs could exceed $1tn per year, and livestock production could decline by 2.6 per cent to 7.5 per cent annually due to AMR, according to Dr. Salih. “In Africa, the situation is particularly alarming, with 37 countries reporting the prevalence of AMR in animal farms, yet only 16 per cent of African countries are conducting routine AMR surveillance in animals as of 2023,” she said.
Dr. Salih also called for urgent action to strengthen leadership, expand surveillance and data systems, promote the responsible use of antimicrobials, improve public and animal health systems, and secure sustainable financing to combat AMR effectively.
Antimicrobial resistance is not just a health issue—it is a threat to our agrifood systems, food safety, food security, livelihoods, and economies
“Our health, our food, and our future depend on the actions we take now,” she stressed.
Dr. Tajudeen said addressing AMR in Africa requires engaging all levels of society in a comprehensive and multi-sectoral approach. “Unless we work together, overcoming antimicrobial resistance will be a difficult and long-drawn process that will cost lives,” he said.
Currently, millions in Africa lack access to essential antibiotics, with a study by Africa CDC and the African Society for Laboratory Medicine revealing that only 1.3 per cent of microbiology labs in 14 member states can test for key AMR pathogens.
The head of the African Society for Laboratory Medicine, Mr. Nqobile Ndlovu, reaffirmed the organization’s commitment to strengthening African laboratory capacities to combat antimicrobial resistance. “Our goal is to ensure the continued efficacy of treatments and promote data-driven solutions to safeguard public health across the continent,” he said.
Dr. Tajudeen underscored the importance of prioritizing infection prevention, strengthening health and food systems, developing human resources, ensuring sustainable access to diagnostics and therapeutics, and investing in laboratory infrastructure for effective surveillance and data generation.
The report recommends an increase in the availability of high-quality diagnostics, vaccines, and antimicrobials for high-priority pathogens in high-risk African countries.