The World Health Organisation has said that about one in 100 children has autism spectrum disorders, which constitute a diverse group of conditions related to the development of the brain.
A neurodivergent clinician at Neurodivergent Insights, Dr. Neff, notes that though girls are diagnosed at lower rates, they have higher risks.
The WHO said the estimate represents an average figure and reported prevalence varies substantially across studies.
It noted that some well-controlled studies have, however, reported substantially higher figures and the prevalence of autism in many low- and middle-income countries is unknown.
people with autism have the right to the enjoyment of the highest attainable standard of physical and mental health
ASDs are characterised by some degree of difficulty with social interaction and communication. Other characteristics are atypical patterns of activities and behaviours, such as difficulty with the transition from one activity to another, a focus on details, and unusual reactions to sensations.
The abilities and needs of autistic people vary and can evolve over time.
“While some people with autism can live independently, others have severe disabilities and require life-long care and support. Autism often has an impact on education and employment opportunities.
“In addition, the demands on families providing care and support can be significant. Societal attitudes and the level of support provided by local and national authorities are important factors determining the quality of life of people with autism.
“Characteristics of autism may be detected in early childhood, but autism is often not diagnosed until much later.
There is no evidence to suggest that any childhood vaccine may increase the risk of autism
“People with autism often have co-occurring conditions, including epilepsy, depression, anxiety, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder as well as challenging behaviours such as difficulty sleeping and self-injury.
“The level of intellectual functioning among autistic people varies widely, extending from profound impairment to superior levels,” WHO said.
It said available scientific evidence suggests that there may be many factors that make a child more likely to have autism, including environmental and genetic factors.
“Available epidemiological data conclude that there is no evidence of a causal association between measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine, and autism. Previous studies suggesting a causal link were found to be filled with methodological flaws.
Persons with autism are often subject to stigma and discrimination, including unjust deprivation of health care, education, and opportunities to engage and participate in their communities
“There is also no evidence to suggest that any other childhood vaccine may increase the risk of autism. Evidence reviews of the potential association between the preservative thiomersal and aluminium adjuvants contained in inactivated vaccines and the risk of autism strongly concluded that vaccines do not increase the risk of autism,” the global health body said.
The organisation said a broad range of interventions, from early childhood, and across the life span, can optimise the development, health, well-being, and quality of life of autistic people.
It noted that people with autism have the right to the enjoyment of the highest attainable standard of physical and mental health, but they are often subject to stigma and discrimination, including unjust deprivation of health care, education, and opportunities to engage and participate in their communities.
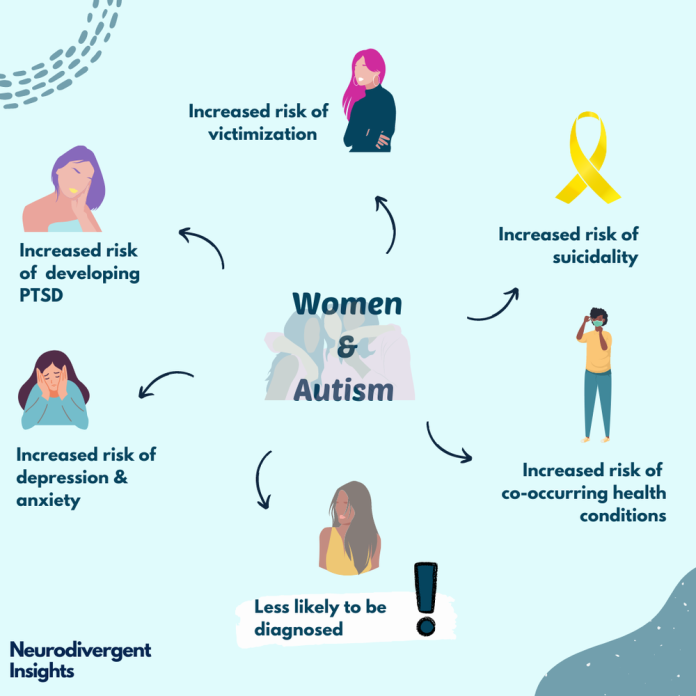
Clinician Neff says women are less likely to be diagnosed, yet more vulnerable to several risks associated with autism. “These risks are magnified for those with additional marginalized identities,” she said.
She added, “A recent study suggests we are missing autistic girls at alarming rates. While the often-cited male-to-female autism ratio is 4:1 McCrossin’s (2022); mathematical projections, which take into consideration diagnostic bias, suggest the true male-to-female ratio is 3:4, with 80% of autistic girls remaining undiagnosed by the age of 18.”
Neff laments that women and girls are more likely to go undetected as their special interests are more likely to culturally blend in as they may be interested in humanitarianism, religion, animals, people, pop culture, etc.
They are also less likely to present with the same social-communication differences and more likely to mask their differences and socially blend in (although they often experience relationship difficulties which make maintaining friendships difficult, Neff contends.
She adds that autistic women are more likely than their neurotypical peers to experience health issues.
“Without an autism diagnosis, it is more likely physical ailments will be minimized, dismissed or untreated,”she said, noting that health issues that are more prevalent among autistic women include:
- Epilepsy
- Endocrine disorders
- Reproductive health issues
- Neurological conditions
- Metabolic disorders
- Gastrointestinal issues
- Nutritional issues
- Immune and autoimmune conditions
- Additionally, Autistic folks have an increased risk of:
- Heart disease
- Cancer