Deciding on a birth control method is a significant and personal choice for women. With the landscape of reproductive health evolving, the importance of understanding each birth control option cannot be overemphasised. It’s not only about preventing pregnancy; it’s also about managing one’s health, lifestyle, and future plans.
Each method comes with its own set of benefits and drawbacks, and what may be ideal for one woman may not suit another. This comprehensive analysis aims to provide a clear and detailed overview of the various birth control methods available, their mechanisms of action, and the inherent pros and cons to empower women in making the best-informed decisions for their reproductive health.
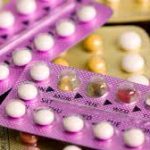
Oral contraceptive (birth control pills)
Overview: Birth control pills are one of the most commonly used methods of contraception. These are hormonal tablets containing estrogen and progestin (or sometimes just progestin) that are taken daily.
Pros:
• Highly effective when used correctly.
• Can improve menstrual cycle regularity.
• May offer benefits such as reduced acne and lowering the risk of certain cancers.
Cons:
• Daily commitment required.
• Can have side effects such as mood swings and blood clots.
• Does not protect against STIs.
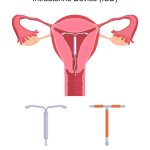 Intrauterine Device (IUD)
Intrauterine Device (IUD)
Overview: An IUD is a small T-shaped device inserted into the uterus by a healthcare professional. There are two types of IUDs: hormonal and copper.
Pros:
• Long-term protection against pregnancy.
• One-time procedure with effects lasting several years.
• Can be reversible.
Cons:
• May cause heavier periods and cramping (particularly copper IUDs).
• Slight risk of the IUD slipping out of place or puncturing the uterine wall.
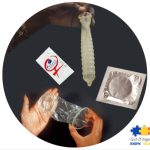
Barrier methods (condoms, diaphragms, etc.)
Overview: Barrier methods include male and female condoms, diaphragms, and cervical caps. They physically block sperm from reaching the egg.
Pros:
• Condoms provide protection against STIs.
• No hormonal side effects.
Cons:
• Must be used correctly every time to be effective.
• Can be less reliable than other methods if not used perfectly.
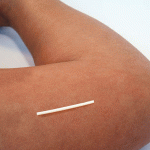
Implants (Implantable rods)
Overview: The implant is a tiny rod inserted under the skin of the upper arm that releases progestin.
Pros:
• Provides continuous protection for up to three years.
• Highly effective and convenient after insertion.
Cons:
• Can cause side effects like menstrual irregularities and weight gain.
• Requires a minor surgical procedure for insertion and removal.
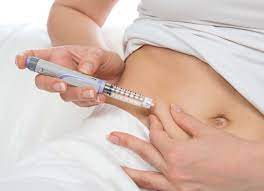
Injectables (Depo-Provera, DMPA-SC, Sayana Press, etc)
Overview: This method involves receiving an injection of the hormone progestin every three months.
Pros:
• Very effective and doesn’t require daily action.
• May reduce menstrual cramps and anemia.
Cons:
• Can cause a delay in the return of fertility after discontinuation.
• Possible side effects include weight gain and bone density loss with long-term use.
Emergency contraception (morning-after pill)
Overview: These pills are intended for use after unprotected intercourse or contraceptive failure. They contain higher doses of the hormones found in regular birth control pills.
Pros:
• Can be used as a backup method if primary contraception fails.
• Available over-the-counter without a prescription.
Cons:
• Not as effective as other forms of contraception and should not be used regularly.
• Can cause side effects like nausea and changes in the menstrual cycle.
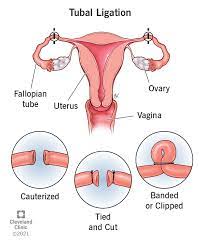
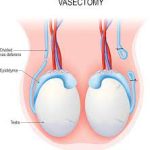
Sterilization (Tubal ligation or vasectomy)
Overview: Sterilization is a permanent method of contraception involving surgical procedures such as tubal ligation for women or vasectomy for men.
Pros:
• Provides a permanent solution with a one-time procedure.
• Highly effective and worry-free once completed.
Cons:
• Surgical risks and potentially irreversible.
• Does not offer protection against STIs.
In conclusion, the selection of a birth control method is a deeply individual decision that must consider medical history, lifestyle preferences, convenience, and personal health goals. Women should discuss with their healthcare providers to weigh the benefits and risks of each option, ensuring a choice that aligns with their well-being and future family planning desires.


