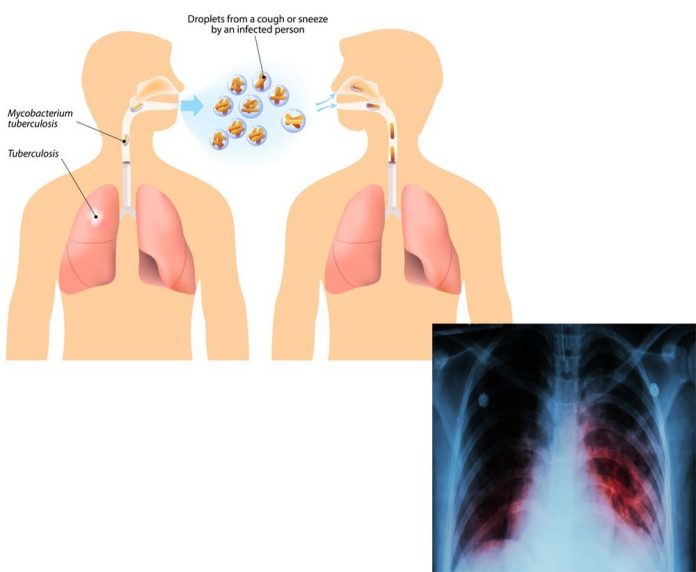
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease that continues to pose a significant threat to public health worldwide. Despite advancements in medical science, it remains one of the top 15 causes of death, with 1.6 million people succumbing to it in 2021, according to the World Health Organization (WHO).
Tuberculosis is gender-blind and it can infect people of any age, hence the need for everyone to beware of its infection and how to avoid being one of the statistics.
What is TB?
According to experts, TB is a bacterial infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It primarily affects the lungs but can impact other organs as well. It spreads through the air when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), TB can exist in two conditions: latent TB infection (where the person does not show symptoms and is not contagious); and TB disease (where the person shows symptoms and can spread the bacteria to others).
Women, especially those in their reproductive years, can experience unique challenges if infected with TB. According to a WHO report, TB is one of the top three causes of death among women aged 15 to 44. Furthermore, it says, pregnant women with active TB may face adverse outcomes such as transmission of the infectious disease to their newborns.
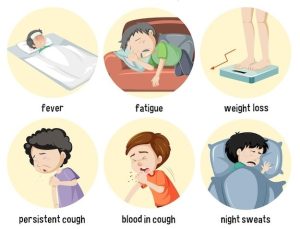
Symptoms of TB
It is necessary to recognize TB symptoms for timely intervention and management. TB, whether latent or active, can manifest differently and it is particularly the active form that demonstrates recognizable symptoms.
These signs, according to the CDC, include:
Persistent cough: A cough that lasts three or more weeks, which may produce discolored or bloody sputum, is a notable sign of TB.
Weight loss: Unexplained weight loss or the inability to gain weight can signal an underlying issue with TB.
Fever and night sweats: A low-grade, persistent fever and night sweats that are not attributed to another condition can also be indicative of TB.
Fatigue and weakness: Persistent fatigue and weakness, even when receiving adequate nutrition and rest, is another symptom to be mindful of.
Chest pain: Chest pain, especially when breathing or coughing, should warrant immediate medical attention as it can be indicative of pulmonary TB.
Shortness of breath: Experiencing difficulty in breathing, even during mild activities, is a symptom to be wary of.
Swollen lymph nodes: Enlarged lymph nodes, particularly in the neck, can be a symptom of extrapulmonary TB.
Loss of appetite: A decrease in appetite or a persistent aversion to food may also be a sign of TB.
If any of these symptoms are noted, it’s paramount to consult healthcare professionals immediately for a thorough examination, as TB, if left untreated or if treatment is delayed, can be fatal. Additionally, considering the risk of transmission, it is equally important to minimize contact with others until a healthcare provider confirms that the condition is not contagious.
pregnant women with active TB may face adverse outcomes such as transmission of the infectious disease to their newborns
Prevention and control
Preventing TB, particularly in environments where it’s common, requires a multifaceted approach, such as:
• Vaccination: The Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccine is widely used to protect against TB and is especially effective in preventing severe forms of the disease in children, according to the Mayo Clinic, a nonprofit American academic medical center focused on integrated clinical practice, education, and research.
• Testing and treatment: Regular TB tests, especially for those at higher risk, can identify latent TB infection before it becomes active. According to CVS, a prominent American healthcare company, if TB is identified at an early stage, it can be treated effectively with antibiotics.
• Healthy lifestyle: Maintaining a strong immune system through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking can act as a defensive wall against TB.
• Wearing masks: In regions where TB is prevalent, wearing masks and ensuring proper ventilation in public spaces can mitigate the risk of transmission.
Community and support
Fostering community support and raising awareness about TB are pivotal in combating its spread. Women can champion TB awareness by engaging in and initiating conversations about its risks, prevention, and treatment within their communities and social circles.
Conclusion
TB continues to be a looming health threat, and its implications for women, especially those aspiring towards a healthier life, are substantial. By understanding its mechanisms, adhering to prevention strategies like vaccination, testing, and leading a healthy lifestyle, and advocating for community awareness, women can forge a path to not only safeguard themselves but also to uplift their communities in the battle against Tuberculosis.