Heart disease, a leading cause of mortality worldwide, poses a significant health challenge.
According to the British Health Foundation, around one in six deaths globally are caused by coronary heart disease.

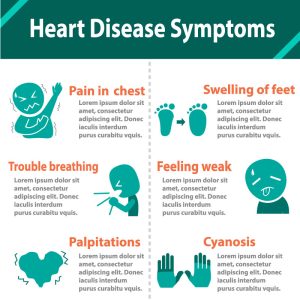 The Foundation says, “Before the coronavirus pandemic, coronary heart disease had been the leading cause of death worldwide for at least 30 years; adding, “Worldwide, coronary heart disease is now killing more people than ever before.”
The Foundation says, “Before the coronavirus pandemic, coronary heart disease had been the leading cause of death worldwide for at least 30 years; adding, “Worldwide, coronary heart disease is now killing more people than ever before.”
Experts, however, say proactive measures based on scientific research can markedly reduce the risk.
This comprehensive guide presents six effective strategies, grounded in scientific evidence, to combat the threat of heart disease.

 Maintain a heart-healthy diet
Maintain a heart-healthy diet
“A balanced diet can reduce the risk of cardiac disease,” as noted in a study by Mahmoud U San of the Department of Medicine, Bayero University, titled, Modifiable cardiovascular risk factors among apparently healthy adult Nigerian population – a cross sectional study.

 Key dietary adjustments include limiting foods that contain saturated fats such as salami, sausages, and any fast/junk foods as recommended by the Mayo Clinic; and reducing sodium [salt] intake to control blood pressure, as per the World Health Organization (WHO).
Key dietary adjustments include limiting foods that contain saturated fats such as salami, sausages, and any fast/junk foods as recommended by the Mayo Clinic; and reducing sodium [salt] intake to control blood pressure, as per the World Health Organization (WHO).
The benefits of omega-3 fatty acids are well-documented in a 2003 WebMD publication titled “What are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?”

 Exercise regularly
Exercise regularly
Physical activity is vital for cardiovascular health. The American Heart Association’s guideline of 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise weekly is based on research like an article by C. I. Ezema, from the University of Nigeria, titled, Blood glucose response to aerobic exercise training program among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
The relationship between regular exercise and reduced heart disease risk is further established in a paper by Adewale L Oyeyemi, from the University of Maiduguri, titled, Relationship of physical activity to cardiovascular risk factors in an urban population of Nigerian adults.

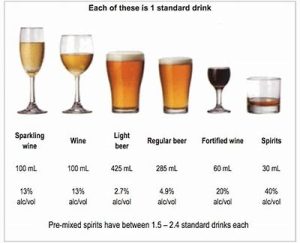
Quit smoking and limit alcohol
Smoking cessation is critical in lowering heart disease risk. This fact is substantiated by a 2020 publication by Iya Eze Bassey and colleagues from the University of Calabar, titled, Cardiovascular Disease risk Factors in Male Cigarette Smokers in Calabar, Southern Nigeria.
Alcohol in moderation is crucial, as excessive intake can lead to high blood pressure and heart failure, according to the WHO.
Kenneth J. Mukamal, M.D., from Harvard Medical School, also discusses “The Effects of Smoking and Drinking on Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Factors” in his paper.
Monitor blood pressure and cholesterol
Monitoring and managing blood pressure and cholesterol are key to preventing heart disease. High levels of either can lead to arterial damage and increased heart risk, as shown in a 2023 Mayo Clinic publication.
Regular check-ups, as recommended by Healthline, along with lifestyle changes and medication if necessary, can effectively control these factors. The significance of managing these health indicators is highlighted in the findings of AHA Journals.

 Maintain a healthy weight
Maintain a healthy weight
Obesity significantly increases the risk of heart disease. Weight loss and maintenance are critical, as highlighted in research from ScienceDirect.
A healthy weight aids in controlling blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and reducing type 2 diabetes risk, another contributor to heart disease.
The correlation between obesity and increased heart disease risk is detailed in publications from the National Institute of Health.


Manage stress
Chronic stress contributes to heart disease. Stress management, through techniques like meditation, deep breathing, and physical activity, is essential.
The impact of stress on heart health and the effectiveness of these management techniques are documented in Healthline and further supported by the National Institute of Health.

Conclusion
Adopting these six lifestyle changes, each backed by scientific research, can substantially lower your risk of heart disease. Incorporating small, evidence-based steps into your daily routine can lead to significant, long-term improvements in heart health and overall well-being.


