A middle-aged woman named Maryam was happily married and had a baby girl one year after.
Excitement filled the air when she discovered she was expecting her second child. However, from the second trimester of her pregnancy, Maryam experienced bleeding.
As days passed, Maryam’s condition worsened. Bleeding became a part of her daily life, and painful contractions added to her agony. She eventually lost the pregnancy. Later at the hospital, she was informed that she had suffered a condition called placenta previa.
After overcoming her grief, she became pregnant for the third time. Again, she experienced bleeding, but this time, she wasted no time. As soon as she experienced the first sign of bleeding, she rushed to her obstetrician. She shared her previous experience and her medical team closely monitored her throughout the pregnancy.
With expert care, she managed to navigate the turbulent waters of placenta previa. The bleeding, although persistent, was controlled through careful medical intervention. The support of her medical team gave her hope. And she had a successful pregnancy outcome.
What is placenta previa?
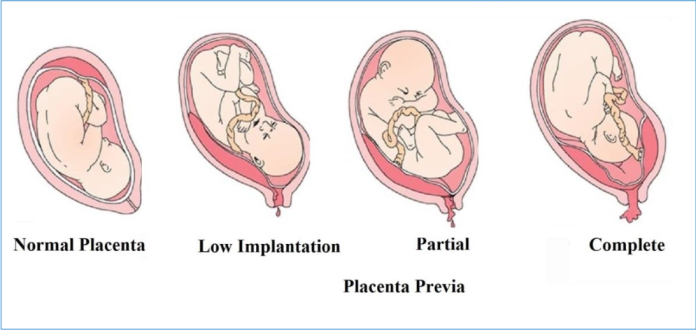
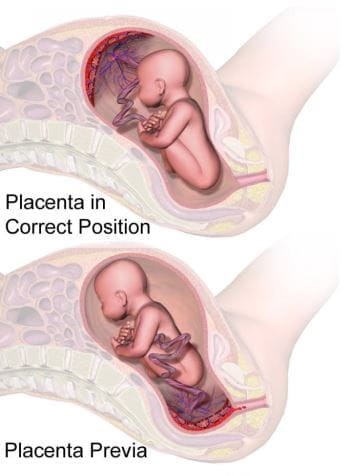
According to experts at Mayo Clinic, placenta previa is a condition during pregnancy where the placenta blocks all or part of the baby’s exit from your vagina — that is, the opening of the uterus (cervix).
Americanpregnancy.org also described placenta previa as a condition where the placenta lies low in the uterus and partially or completely covers the cervix. The placenta may also separate from the uterine wall as the cervix begins to dilate during labour.
Many people are unaware of this condition, its symptoms, and the necessary management strategies. Yet, it can lead to significant bleeding during pregnancy and childbirth, posing potential risks to both mother and baby.
The placenta is an organ that develops inside the uterus during pregnancy. It provides oxygen and nutrition to the baby and also removeswaste. It also connects you to your baby through the umbilical cord.
placenta previa occurs in about one in 200 pregnancies
Typically, the placenta is attached to the top or side of the inner wall of the uterus (womb), but with placenta previa, the placenta attaches lower in the uterus. This results in some portion of the placental tissue covering the cervix and can result in bleeding during the pregnancy or during or after delivery.
Risk factors of placenta previa
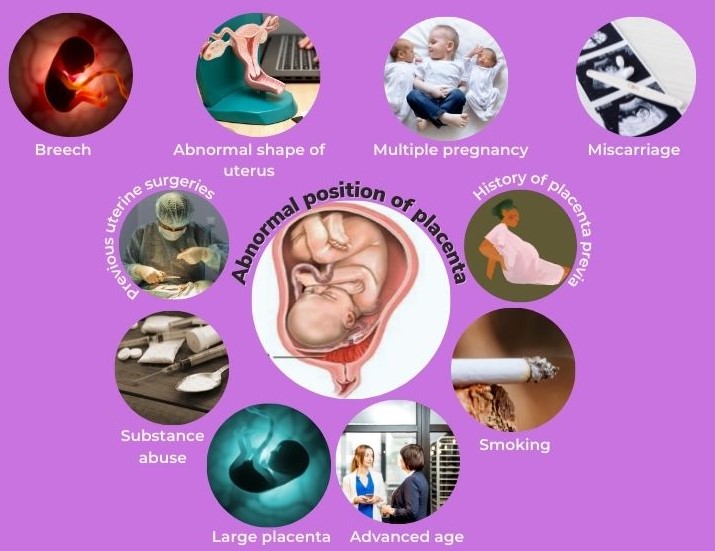
Medical experts admit that the cause of placenta previa is unknown, but among other factors, it is common with previous history of placenta previa, and also found to be associated with women with previously scarred uterus, such as from previous surgery including caesarean deliveries, uterine fibroid surgeries, and dilation and curettage (D&C).
It is also common in women aged 35 and above, women carrying multifetal pregnancy (twins and more) and women who have had more than one pregnancy in the past.
Experts at Mayo Clinic also the condition is common among women who have had Assisted Reproductive Technology such as IVF; and women who smoke or use cocaine.
Experts say placenta previa occurs in about one in 200 pregnancies.
Possible complications of placenta previa
Cleveland Clinic says there are risks for both mother and baby as a result of complications from placenta previa.
For mother:
- Severe bleeding can occur during pregnancy, labour or delivery.
- Early birth: If you’re bleeding severely, your healthcare provider may perform an emergency C-section before your baby is full term (40 weeks).
- Blood loss: Anaemia, low blood pressure, pale skin or shortness of breath are all side effects of losing too much blood.
- Placenta accreta: This is when the placenta grows too deeply in the wall of your uterus. This can cause severe bleeding after delivery.
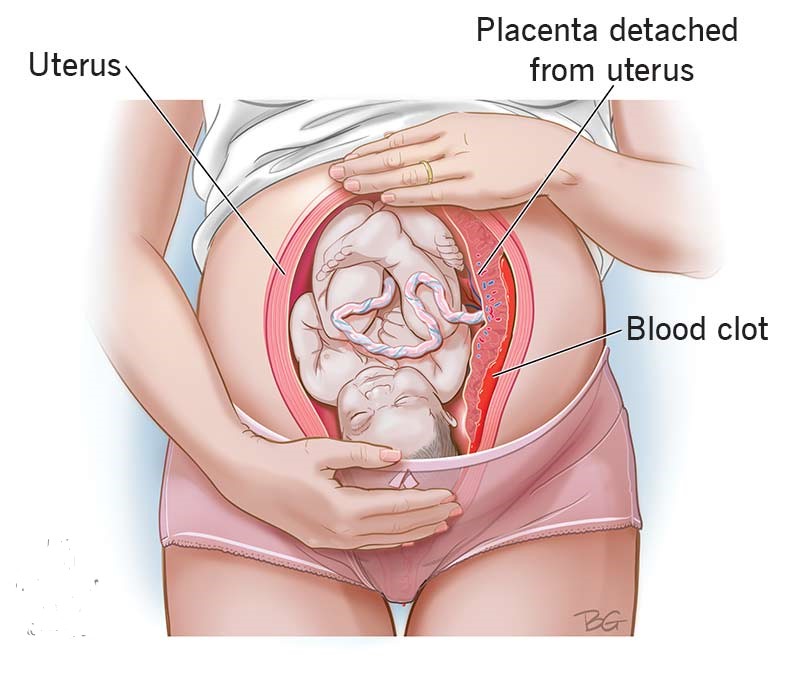
- Placental abruption: This is when the placenta separates from the uterus before the baby is born. This decreases the baby’s supply of oxygen and nutrients.
women are encouraged to begin antenatal care as soon as pregnancy is suspected.
- For baby:
- Premature birth: If the bleeding is severe and the mother needs an emergency C-section, the baby may be born too early.
- Low birth weight: This may mean trouble staying warm as poor weight gain is a potential side effect of low birth weight.
- Respiratory issues: Underdeveloped lungs could make breathing more difficult.
When to see a doctor
Pregnant women are encouraged to avail themselves of antenatal care services as soon as pregnancy is suspected.
This allows for routine ultrasound scan that can detect placenta previa even when there are no symptoms in the earliest time possible and the appropriate management instituted.
However, women experiencing bleeding in pregnancy, irrespective of the quantity, must see a doctor as soon as possible for evaluation and diagnosis.